The internet is constantly evolving to improve user experience, and website accessibility is no exception. After performing some usability sessions of our own, we've come to realize how difficult it can be to navigate some websites. As an industry, we need to help spread the word and educate organizations on the importance of ADA compliance for website accessibility. Not just to avoid being sued, but because it's the right thing to do.
In this blog post, we'll discuss the importance of website accessibility and how you can make your website ADA compliant.
Why Consider Website Accessibility?
- It’s the law (kinda/sorta)
- It’s our responsibility
- It’s the right thing to do

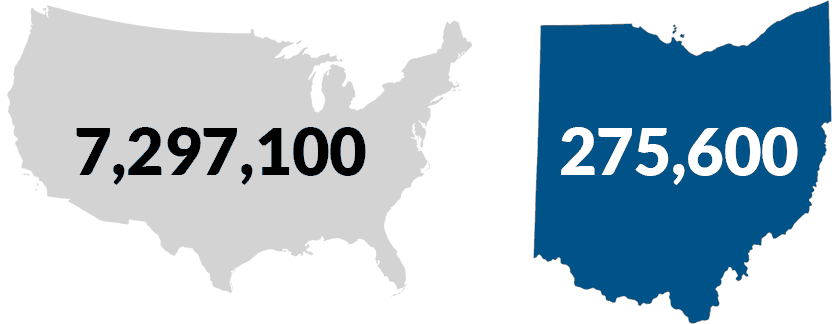
Visual Disability Stats & Figures
2015 Prevalence of Visual Disability
Provided by National Federation of the Blind
Understanding Visual Disabilities
1. Total Blindness
2. Low Vision
Challenges with small text and contrast.
3. Color Blindness
Red-green deficiencies are the most common.

How Did We Get Here?
1973
Rehabilitation Act
The Rehabilitation Act of 1973, as Amended (RehabAct) prohibits discrimination on the basis of disability in programs conducted by federal agencies, in programs receiving federal financial assistance, in federal employment and in the employment practices of federal contractors.
Source: https://www.ada.gov/cguide.htm?#anchor65610
1990
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) became law in 1990. The ADA is a civil rights law that prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities in all areas of public life, including jobs, schools, transportation, and all public and private places that are open to the general public. The purpose of the law is to make sure that people with disabilities have the same rights and opportunities as everyone else. The ADA gives civil rights protections to individuals with disabilities similar to those provided to individuals on the basis of race, color, sex, national origin, age, and religion. It guarantees equal opportunity for individuals with disabilities in public accommodations, employment, transportation, state and local government services, and telecommunications. The ADA is divided into five titles (or sections) that relate to different areas of public life.
Source: https://www.ada.gov/cguide.htm?#anchor62335
1998
Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act
Congress amended the Rehabilitation Act to require Federal agencies to make their electronic information accessible to people with disabilities.
Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act
Requires organizations that receive federal funding or grants to have accessible online content.
Source: https://www.ada.gov/cguide.htm?#anchor65610
2010
DOJ proposes regulations governing access to websites under the ADA Act
2015
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Standards
The U.S. Access Board submitted an official ICT guidelines refresh that points to WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) 2.0 Level AA as the compliance standard.
2017
Vision-impaired plaintiff wins the first trial on ADA web accessibility
In June 2017, a federal judge in Florida issued a verdict in favor of a customer who had sued the grocery chain, claiming it violated the Americans With Disabilities Act because its websites were not accessible to blind and vision-impaired users. This is believed to be the first trial verdict in a website ADA lawsuit.
Proposed regulations for 2018 put on hold by Trump administration
Source: http://www.pepperlaw.com/publications/doj-puts-ada-website-project-on-hold-2017-08-02/
Where Do I Go From Here?
You have two options to consider:
- Make your website ADA compliant - Implement all items listed in WCAG 2.0 AA
- Go beyond compliance - There are potential issues that aren’t detected through an automated ADA audit that can help improve user experience. We'll explain in more detail below.

Is My Website ADA Compliant?
Unless your website was built specifically for ADA compliance, it's likely not 100% compliant.
So how do I find out if my site is compliant?
- Hire professionals. Hire a web company that has experience with ADA compliance and have them do an audit for you.
- DIY. Use a desktop or Mobile simulator app or the most widely used ADA compliance website checker: http://wave.webaim.org.
- Usability sessions. Partner with your local blind center and see if they have volunteers who are willing to go through your website and provide feedback.
Website Accessibility Desktop Simulator
NVDA for Windows
This is a free tool that is easy to set up. You can even run it from a USB drive so you don’t have to download it to your PC. Windows also has built-in settings, but these can be difficult to setup. Google Chrome also has a plugin called "CHROMEVOX."
Additional Sources:
Website Accessibility Mobile Simulators
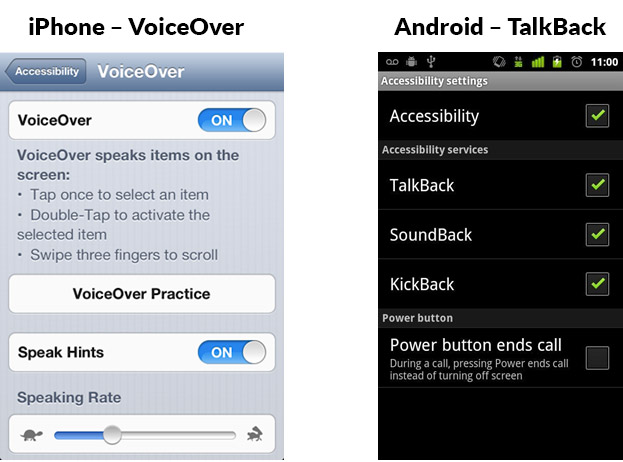
iPhone – VoiceOver
According to a 2015 WebAIM study, VoiceOver is the top app used by those who are visually impaired. It’s free and easy to turn on and off. Turn VoiceOver on and you’ll get a good simulation of your website experience using VoiceOver.
How to activate VoiceOver on your iPhone or iPad
- Launch the Settings app from your Home screen.
- Tap on General.
- Tap on Accessibility.
- Tap on VoiceOver under the Vision category at the top.
- Tap the switch next to VoiceOver to enable it.
Android – TalkBack
This comes pre-installed on most Android devices.
How to active TalkBack
- Open your device's Settings app.
- Open Accessibility, then TalkBack.
- Turn on TalkBack.
- In the confirmation dialog, tap OK.
ADA Website Accessibility Guidelines
There are two sets of current guidelines to consider.
The current 508 law (published in 2000) is very outdated and references web technology from the late 1990's. If you follow the more current WCAG 2.0, you will be in a better position to be compliant down the road. These newer guidelines cover what’s included in the 508 law and much more.
Section 508 ADA Website Accessibility Guidelines
(a) A text equivalent for every non-text element shall be provided (e.g., via “alt”, “longdesc”, or in element content).
(b) Equivalent alternatives for any multimedia presentation shall be synchronized with the presentation.
(c) Web pages shall be designed so that all information conveyed with color is also available without color, for example from context or markup.
(d) Documents shall be organized so they are readable without requiring an associated style sheet.
(e) Redundant text links shall be provided for each active region of a server-side image map.
(f) Client-side image maps shall be provided instead of server-side image maps except where the regions cannot be defined with an available geometric shape.
(g) Row and column headers shall be identified for data tables.
(h) Markup shall be used to associate data cells and header cells for data tables that have two or more logical levels of row or column headers.
(i) Frames shall be titled with text that facilitates frame identification and navigation.
WCAG 2.0 Guidelines
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.0
Published by W3C, the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines serve to make digital content accessible for all users, including those with disabilities.
WCAG 2.0 guidelines include three levels of compliance:
- Level A is the highest priority and usually the easiest to achieve.
- Level AA is more comprehensive. (This appears to be the GOLD standard for compliance).
- Level AAA is the strictest, most comprehensive accessible design.
Source: https://www.w3.org/TR/WCAG20/
POUR – 4 Main Principles of Accessibility
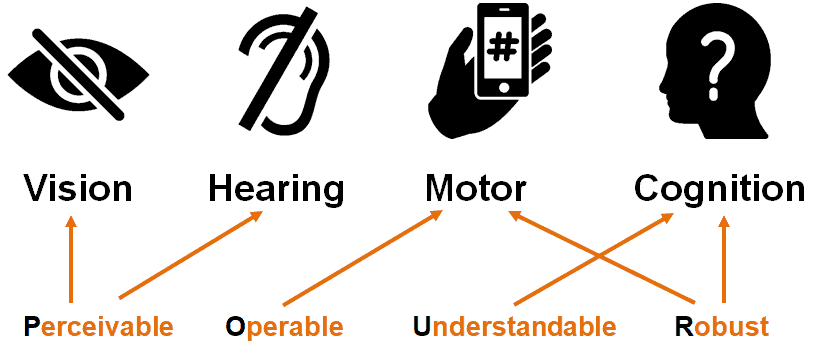
Perceivable: pertains to visual information (graphics/color/layout)
Operable: pertains to navigation (keyboard/tabbing)
Understandable: pertains to illogical linear order
Robust: pertains to difficult technologies/functionality (JavaScript, Flash, etc.)
Source: https://webaim.org/articles/pour/
ADA Website Accessibility Guidelines
Resource for ADA compliant web design
Key Concepts for Blindness
Navigation - Users generally do not use a mouse.
SOLUTION - Don't write scripts that require mouse usage. Supply keyboard alternatives.
ALT tags - Images, photos, graphics are unusable.
SOLUTION - Provide text descriptions in alt text and, if necessary, longer explanations (either on the same page or with a link to another page). Collaborate with your SEO team as they may have a specific keyword they are targeting.
Links - Users often jump from link to link using the Tab key. PDF links - Let users know if a link will open a PDF file.
SOLUTION - Make sure that links make sense out of context ("click here" is problematic). Always add a title tag to each link.
Frames - Cannot be "seen" all at once. They must be visited separately, which can lead to disorientation.
SOLUTION - Don't use frames unless you have to. If you use them, provide frame titles that communicate their purpose (e.g. "navigational frame", "main content").
Tables - It may be difficult for users to tell where they are when listening to table cell contents.
SOLUTION - Providing column and row headers (<th>) helps users make sense of these when read row by row from left to right.
Complex tables and graphs - Items like this that are usually interpreted visually are unusable.
SOLUTION - Provide summaries and/or text descriptions.
Image maps - Not all screen readers support these.
SOLUTION - Supply redundant text links for hot spots in image maps.
Page titles - Every page should have a unique title.
SOLUTION - Due to your CMS, this may be an issue for some pages that are dynamically generated and don’t give you the control to customize every view/page. Collaborate with your SEO team.
Key Concepts for Low Vision
Text in graphics - This text does not enlarge without special software, and looks pixelated when enlarged. Users may set their own font and background colors.
SOLUTION - Limit or eliminate text within graphics. Allow them to do so by using as much real text as possible, rather than text within graphics.
Font sizes - Screen magnifiers reduce the usable window size.
SOLUTION - To reduce that amount of horizontal scrolling, use relative rather than absolute units (e.g. use percentages for table widths instead of pixels).
Key Concepts for Color Blindness
Reds and greens - These colors are often indistinguishable.
SOLUTION - This is not normally a problem except in cases where the colors convey important information.
Other colors - These colors may be indistinguishable.
SOLUTION - This is not normally a problem except in cases where the colors convey important information.
Color contrast - On many websites, this is an issue that needs addressed.
SOLUTION - Especially with smaller font sizes, make sure to have enough color contrast between foreground and background colors. Stay away from "Orange" as this is the most challenging color to work with as a web designer. Resource for using ADA-safe colors on the web.
Other Items to Consider - Going Beyond Compliance
Site navigation - Traditional drop-down menus in the header of every page can be a challenge for the visually impaired.
SOLUTION - If possible, provide a “skip navigation” link at the top of every page. That takes the user directly to the content on the page. Here are a few examples of this treatment:
- https://www.sos.state.oh.us/ - see upper left area of header area
- https://www.akronmetro.org/ - use the tab key and you'll see a skip navigation button appear (only appears for screen readers)
Mobile menus - These can be problematic.
SOLUTION - Make sure to do thorough user/simulator testing.
Forms - Screen readers can have a difficult time with forms.
SOLUTION - Ensure all form fields have labels. If using CAPTCHA, make sure it can be read. Ensure users understand which fields are required and that error messages can be read.
How Do I Make Audio and Video ADA Compliant?
- Transcript - Required.
- Captions - Nice to have for most W3C media; Required for some.
- Audio Description - Required only for relevant visuals not already covered in what's said.
- Sign Language - Not required for W3C multimedia.
Resource for Video Accessibility
How Do I Make PDFs ADA Compliant?
One of the most overlooked items in the ADA compliance checklist is PDFs. Yes, these need to be compliant and able to be read by a screen reader. PDFs are abundant on websites, so please don't forget to work through the checklist below. It's pretty easy once you get a process in place. Just make sure you train all website content providers to follow these guidelines.
TIP: All Microsoft products like WORD, PowerPoint, etc., have the ability to check for ADA compliance before exporting your document as a PDF.
- Images - All images need to have ALT tags.
- Enable accessibility - PDF conversion settings need to be properly set; “Enable accessibility” needs to be checked.
- Enable text access - Make sure “screen reader devices for the visually impaired” is checked.
- Title - Make sure the “Title:” and “Author:” areas are filled out with the proper information.
- Language - Make sure “Language:” is selected: English U.S.
- File names - When saving PDFs, never use spaces. Always use hyphens or underscores to represent spaces for file names.
Resource for PDF accessibility

Next Steps: You’re ADA Compliant, Now What?
- Get your team on board
- Get a process in place
- Create a work flow with approvals
- Create training documents
- Hold training sessions
- Stay compliant
Resources:
- The ultimate ADA web compliance resource - http://webaim.org
- ADA compliance audit tool - http://wave.webaim.org
- NVDA download, desktop simulator app - https://en.softonic.com/download/nvda/windows/post-download?sl=1
- Section 508 standards - https://www.access-board.gov/guidelines-and-standards/communications-and-it/about-the-section-508-standards/section-508-standards
- WGAC 2.0 guidelines - https://www.3playmedia.com/2016/02/24/wcag-2-0-the-international-standard-for-web-accessibility-and-inclusive-design/
- Video accessibility - https://www.w3.org/2008/06/video-notes
- Skip navigation information - https://webaim.org/techniques/skipnav/
- Skip navigation sample - https://www.sos.state.oh.us/
- How to code for ADA compliance - https://designsystem.digital.gov
- How to fix font icons for ADA compliance - http://fontawesome.io/accessibility/
- Visually impaired statistics - https://nfb.org/blindness-statistics
- Article about a 2017 ADA compliance lawsuit - http://associationsnow.com/2017/07/website-accessiblity-legal-precedent/